Male Infertility

Male infertility is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of couples worldwide. While infertility is commonly associated with female factors, male infertility contributes to nearly half of all cases of infertility. Understanding the types, causes, and treatment options for male infertility is crucial in addressing this issue and helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood.
Types of Male Infertility:
Male infertility can manifest in various forms, each with its own distinct characteristics. The primary types of male infertility include:
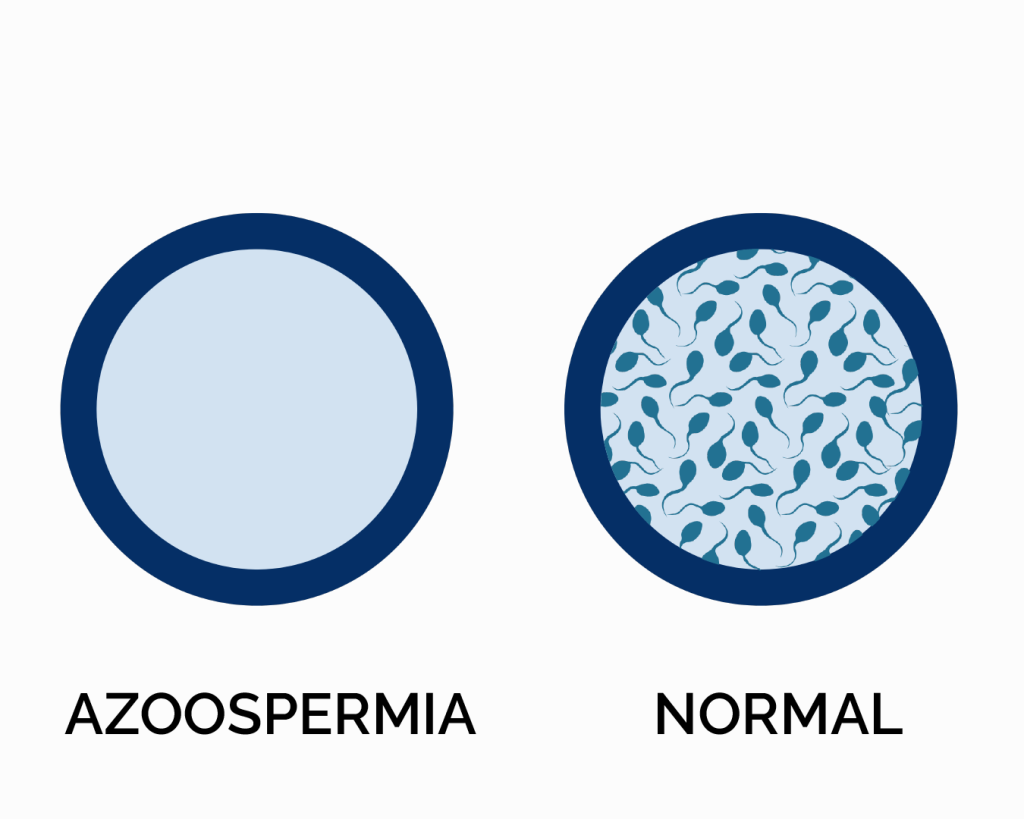
Azoospermia: This condition occurs when a man produces little to no sperm in his semen. Azoospermia can be further classified into obstructive azoospermia, where there is a physical blockage preventing sperm from reaching the ejaculate, and non-obstructive azoospermia, which occurs due to problems with sperm production in the testes.
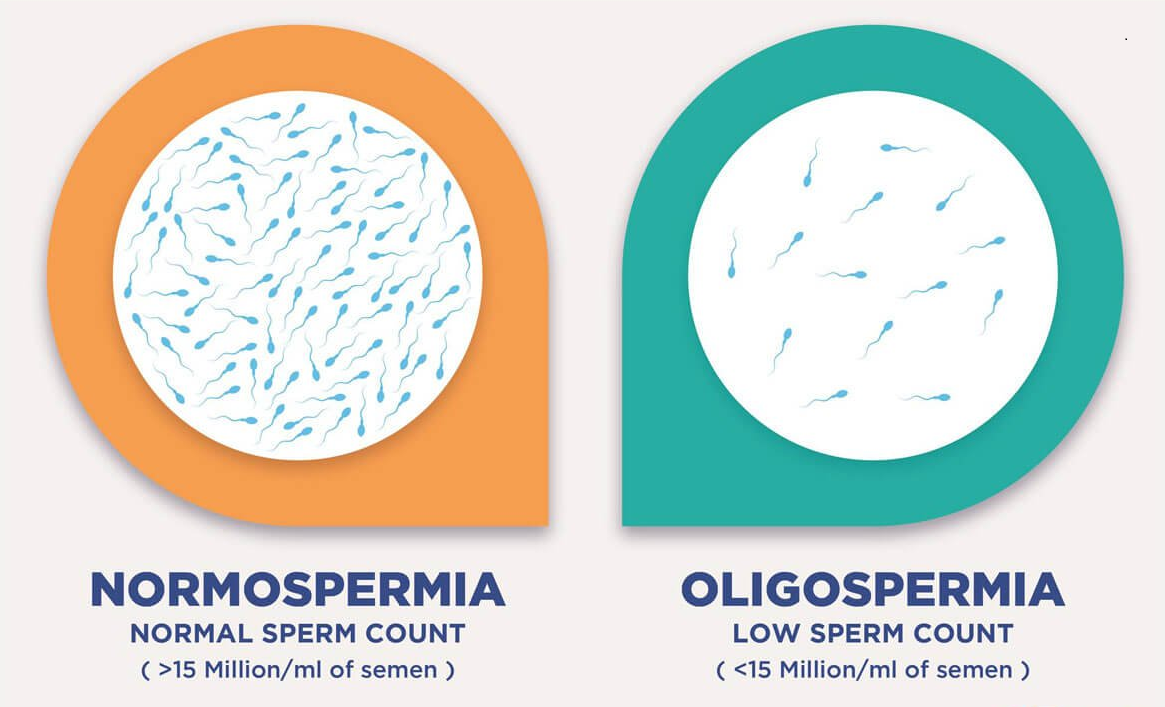
Oligozoospermia: Oligozoospermia is characterized by a low sperm count in the ejaculate. While some sperm are present, their numbers are insufficient for successful fertilization.
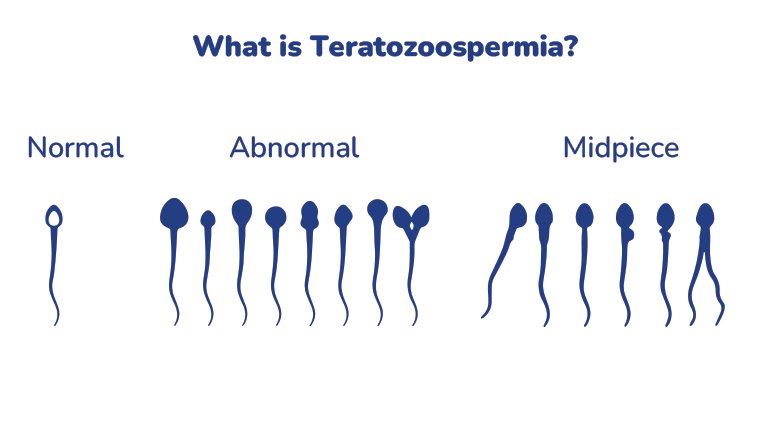
Teratozoospermia: Teratozoospermia refers to abnormalities in sperm morphology, where a significant portion of sperm have abnormal shapes or sizes. These abnormalities can impair sperm motility and hinder their ability to fertilize an egg.
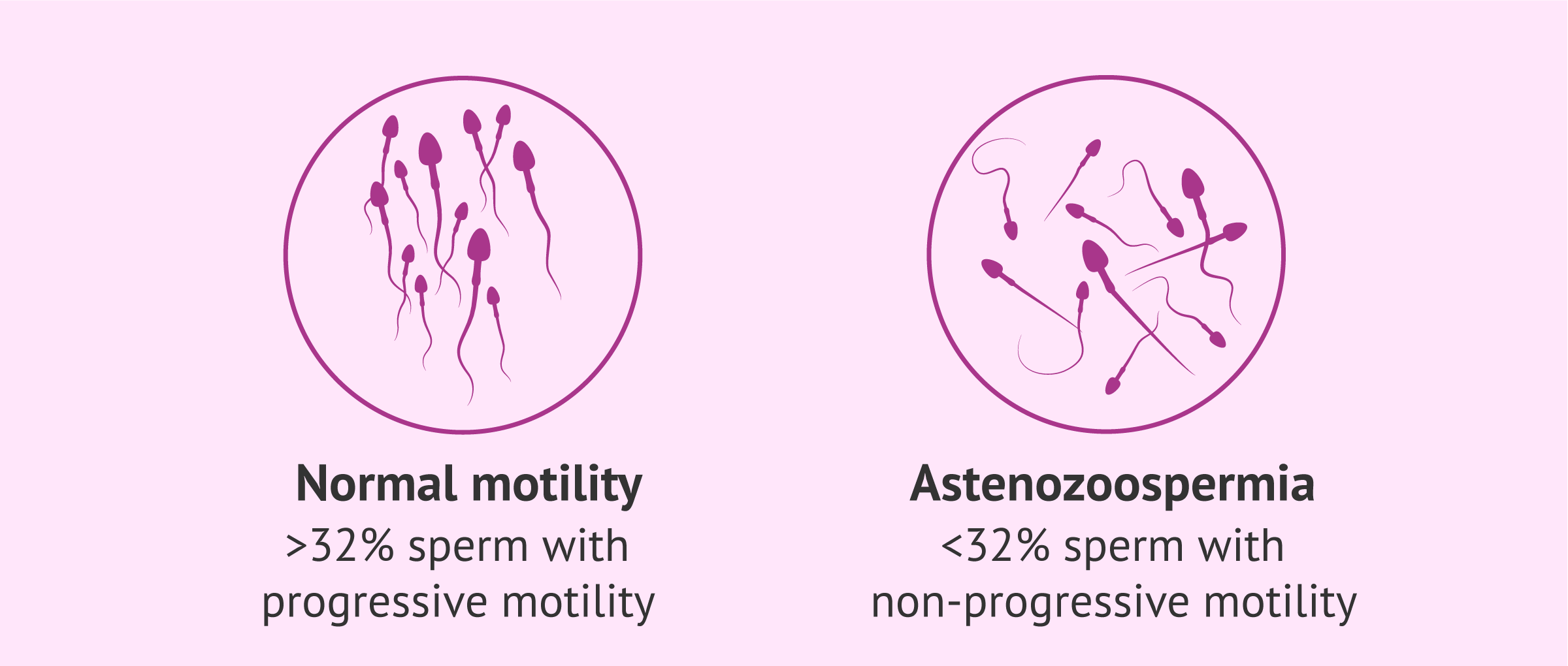
Asthenozoospermia: Asthenozoospermia is characterized by reduced sperm motility, meaning that sperm have difficulty swimming effectively towards the egg for fertilization.
Causes of Male Infertility:
Male infertility can stem from a variety of factors, both physiological and environmental. Some common causes include:
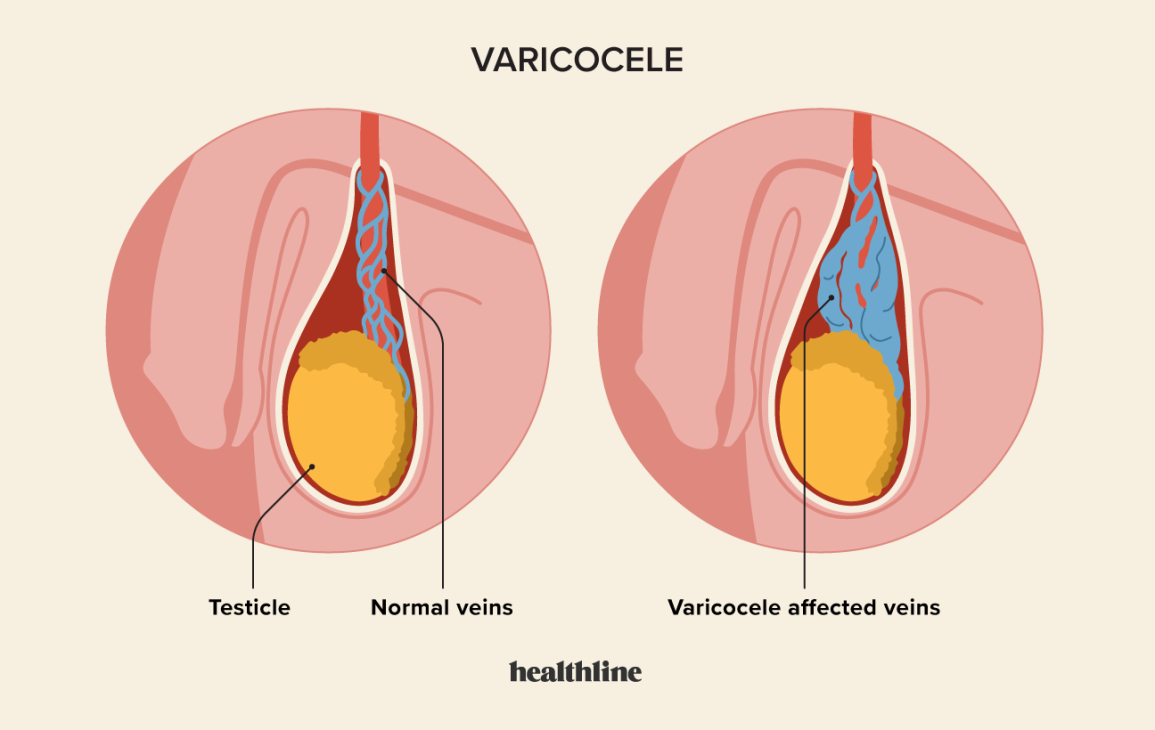
Varicocele: Varicocele is the enlargement of veins within the scrotum, which can lead to overheating of the testicles and impaired sperm production.

Hormonal Imbalances: Disruptions in hormone levels, such as low testosterone or high levels of prolactin, can affect sperm production and quality.
Genetic Factors: Genetic abnormalities, such as Y-chromosome microdeletions or chromosomal anomalies, can impact sperm production and function.

Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices, such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, obesity, and stress, can negatively impact sperm health and fertility.
Infections: Certain infections, such as sexually transmitted infections or reproductive tract infections, can damage sperm production or block sperm transport.

Treatment Approaches for Male Infertility:
Treatment for male infertility depends on the underlying cause and may involve a combination of medical, surgical, or assisted reproductive techniques. Some common treatment approaches include:
Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise, a balanced diet, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and managing stress, can improve sperm quality and fertility.
Medication: Hormonal imbalances or reproductive tract infections may be treated with medications to restore normal function and sperm production.
Surgical Interventions: Surgical procedures, such as varicocele repair to correct enlarged veins in the scrotum or vasectomy reversal to restore sperm flow, may be necessary in certain cases.
Assisted Reproductive Techniques (ART): ART procedures, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilization (IVF) with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), can bypass natural barriers to fertilization and improve the chances of conception.
Sperm Retrieval: In cases of obstructive azoospermia or severe male factor infertility, sperm can be retrieved directly from the testes or epididymis through procedures like testicular sperm extraction (TESE) or percutaneous epididymal sperm aspiration (PESA) for use in ART.
Share :